—95→
The text presented here, which has never before been reprinted, has claims to be the founding document of Don Quijote scholarship -on the topic, still debated after two centuries, of how the work should be edited. This Letter appeared in 1777 as an announcement of John Bowle’s edition of Don Quijote, published four years later. Bowle’s edition, still valued by Quijote scholars, was not only the first annotated edition. It was also the first for which multiple editions were collated, the first to annotate emendations to the text, the first with numbered lines, and the first to have an index.
In the interests of accessibility and readability, this Letter has been modernized throughout, and errors -whether typographical or misspellings by Bowle- have been corrected, usually tacitly. The texts he quotes have been modernized as well. Bowle writes «shews», «cotemporary», «justs», «Dutchess», and «Quixote»; these become «shows», «contemporary», «jousts», «Duchess», and «Quijote». Feijoo’s Theatro critico has become Teatro crítico. The use of capitals, punctuation, italic, and division into paragraphs are also modern, as are the subheadings at the beginning of many paragraphs. The English translations of quotations in Spanish have been omitted, but I have supplied what Bowle believed superfluous, translations of the quotations in Latin. I have suppressed as —96→ unnecessary Bowle’s use of «folio» and «quarto» in bibliographical descriptions. References to the text of Don Quijote have been standardized, supplying part and chapter number.
In some cases I have added information in footnotes, or clarified Bowle’s bibliographical references. My material in notes is marked with brackets: [ ].
For information on the Hispanist work of Percy and Bowle, see the following:
Bowle, John, and Thomas Percy. Cervantine Correspondence. Ed. Daniel Eisenberg. Exeter: University of Exeter, 1987.
Cox, R. Merritt. An English «Ilustrado»: The Reverend John Bowle. Bern, Frankfurt am Main, Las Vegas: Peter Lang, 1977.
Cox, R. Merritt. The Rev. John Bowle. The Genesis of Cervantean Criticism. University of North Carolina Studies in the Romance Languages and Literatures, 99. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1971.
Deyermond, Alan. «Sánchez's Colección and Percy's Reliques: The Editing of Medieval Poetry in the Dawn of Romanticism», Spain and its Literature. Essays in Memory of E. Allison Peers, ed. Ann L Mackenzie (n. p.: Liverpool University Press-Modern Humanities Research Association, 1997), pp. 171–209.
Rico, Francisco. «Historia del texto». Don Quijote, ed. Francisco Rico, segunda edición revisada (Barcelona: Crítica, 1998), I, cxcii-ccxlii, especially pp. ccxvi-ccxviii.
For their assistance with editorial questions, modernization, and proofreading, I would like to thank Dan Clouse, Steve Soud, and Gloria Allaire.
Daniel Eisenberg
Excelsior College
—[97]→A
LETTER
TO THE
Reverend D.r PERCY,
CONCERNING
A NEW AND CLASSICAL EDITION
OF
HISTORIA DEL VALEROSO CAVALLERO
DON QUIJOTE DE LA MANCHA.
To be illustrated by
ANNOTATIONS, and EXTRACTS from the Historians, Poets, and Romances of Spain and Italy, and other Writers Ancient and Modern; with a GLOSSARY, and INDEXES.
In which are occasionally interspersed
Some Reflections on the LEARNING and GENIUS of the AUTHOR.
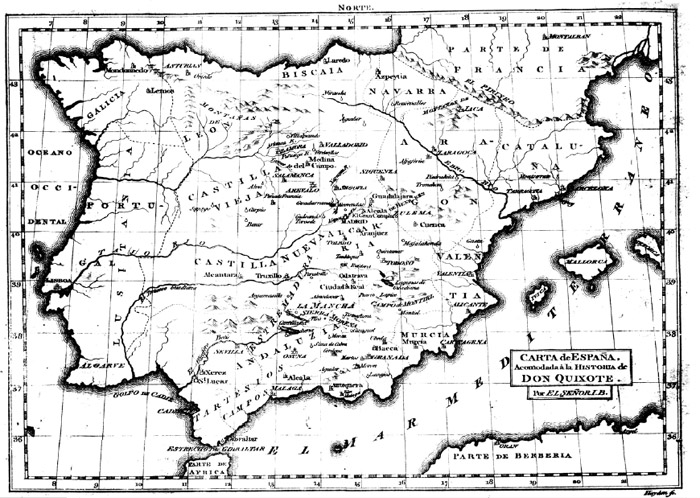
With a MAP OF SPAIN, adapted to the History, and to every Translation of it.
| By the Reverend JOHN BOWLE, M.A. F.S.A. |
|
MIGUEL DE CERVANTES mérite quelque distinction. S'il avait eu l'honneur d'être un Ancien et que son Ouvrage
eût été écrit en Grec ou seulement en Latin, il y a déjà long-temps qu'il aurait eu des Scholiastes et même des
Commentateurs en forme. Avertissement à TIRANT LE BLANC. |
LONDON:
Printed for B. White, Horace's Head, FleetStreet.
MDCCLXXVII.
—98→At length, Dear Sir, I take the liberty thus publicly to acquaint you with the result of my labours on our favourite writer CERVANTES. I particularly address myself to you, as you are so conversant in every branch of polite literature, most especially that which has engrossed so much of my time and attention.
From the commencement of my intimacy with the text of Don Quijote, I was induced to consider the great author as a classic, and to treat him as such. With this view I had the courage to begin and, what is more, the perseverance to finish two most copious verbal indexes to both parts of that celebrated work, on transcribing which it seemed altogether right to sever the proper names of men, places, and other remarkable things, and to make them distinct parts. This has also been done, with this farther addition, that where the name occurs in both parts, the whole is to be found in the former, so that every particular respecting any person, city, mountain, or whatever else is mentioned by the author from ancient and modern history, may be perused together. Thus, for instance, Amadís de Gaula, whom the knight more immediately intended for the grand object of his imitation, besides the introductory verses ascribed to him occurs in fourteen different chapters in the first, and in eight in the second part. The citations will abundantly gratify the pursuits of the most diligent searcher. The several articles under this head, you will probably be surprised to hear, are in number above one thousand, notwithstanding nothing is said of that odious and detestable character of the intolerant Eclesiástico, who is justly held up as an object of contempt and ridicule, and therefore deservedly anonymous. But notwithstanding this, every passage relating to him may be easily found in the —99→ words eclesiástico and religioso, in the general index68.
From this minute survey the necessity of a comment and annotations becomes apparent, as it is of very little use to read what we do not understand. This will be found to be the case in many instances as to the text, which in many places is very obscure. In others our ideas must be very imperfect, and frequently defective, from the want of that collateral assistance which is to be derived from history, from the romances, and other books which, if Cervantes did not immediately consult, will be found to contain matter that will throw light on various passages in his work.
Of some great events which happened in his own time he is to be considered as the original historian. Such were the battle of Lepanto, the taking of the Goleta (I, 39 and 42), and the expulsion of the Moors from Spain, with several lesser incidents to which he alludes, many of which will be verified by the concurrent testimony of other contemporary writers, and will occasionally appear in the notes.
It is not at present my intention to trouble you with extracts
from those libros de caballerías, the romances which, by your assistance,
I have had the patience to toil through, but shall in general
observe that the secondary amends for the drudgery of such
painful reading has been what Monsieur de St. Palaye and other
French writers on the history of chivalry have remarked: the
faithful and exact descriptions of the manners and customs of the
times in which they were wrote. Though the facts related were in
themselves as fabulous as the heroes of whom they were told, yet
similar events frequently occurred. In this respect they deserve
some esteem as histories, because these latter enumerate several
facts similar to those they particularly mention. Thus, for example,
the watching of arms in some church or chapel previous to the
receiving the order of knighthood, with its various ceremonies of
—100→
creation, the hearing mass and confession69 before the day of battle,
with other religious circumstances, are to be found both in history
and romance, though perhaps more frequently and more copiously
in the latter. And here, when the same fact occurs in almost
every writer, we may safely infer that such practice was universal.
Thus the parting of the sun betwixt the combatants, that it might
not affect the one more than the other (Quijote II, 56), and which
will be shown at large in the notes, was constantly in use. As
general was that specimen of knightly courtesy used by Quijote,
of leading the duchess her horse by the bridle: «de puro cortés y
comedido tomó la rienda de su palafrén»
(II, 34). This was a very
ancient custom, and continued long in use. It most probably began
with the clergy, for Pepin, King of France, with his son Charlemagne,
and his other children, besides prostrating themselves at
the feet of Pope Stephen, led his mule by the reins as he approached
Paris. This happened after the middle of the eighth century70. So
don Fernando, King of Aragon, who distinguished himself by his
extraordinary attachment and civility to the Anti-Pope Benedict
the Thirteenth, led the horse on which he rode under a canopy to
the church at Morella in Valencia. This happened in the year 1414,
as we are informed by Mariana (Libro 20, cap. 6). So, the same
historian tells us, Henry King of Castille treated his sister the infanta
Doña Isabela, the wife of the same king, who was afterwards his
successor, in Segovia, in 1474: «la infanta salió a pasear por las
calles de la ciudad en un palafrén, que él mismo tomó de las
riendas, para más honrralla»
.
But what is most to our purpose, is the continuance of it to our
author's own time. Margaret of Austria, queen of Philip the Third,
when she made her public entry into Valencia, left her coach and
mounted her hackney, which, in place of reins, had two long cords
of red silk and gold, and these were held by some nobles and
—101→
principal lords of the kingdom, and by certain officers of high rank
and distinction. «La hacanea de la reina tenía dos cordones largos
de seda colorada y oro, que servían como de riendas, y éstos los
llevaban de una parte los varones y señores principales del reino,
y de la otra los oficiales que llaman del quitamiento»
71.
It is natural for writers to specify customs and fashions that
generally prevail in their own times. These necessarily fall from
their pens, accidentally and unintentionally. What has suggested
this reflection is the naming of Milan in one or two places as the
scene of dress and gallantry. The captive mentions (I, 39) his
setting off from Genoa to furnish himself with arms, and some fine
clothes as a soldier: «llegué con próspero viaje a Génoa; fui desde
allí a Milán, donde me acomodé de armas, y de algunas galas de
soldado»
. It is to our purpose, and worthy of notice, that this city
preceded France and led the van in the articles of fashion, sumptuous
and gaudy apparel, jewelry, and pompous luxury in various
shapes, before her European neighbours. As early as the famed
interview between Henry the Eighth and Francis the First, at
Guisnes, at one of the masques there, ten ladies were attired after
the fashion of Millaine, in rich tissue and cloth of silver raised,
parted, travers, and ruffed sleeves, with foresleeves pendant, knit
with points of gold, and cowls or coifs of gold piped72, and Millaine
bonnets of crimson satin drawn through with cloth of gold73. Two
years after, at one of Wolsey's banquets, «eight ladies had Millian
gowns of white satin; on their heads, cowls and Millian bonnets of
gold with jewels»
74. Though these last citations affect female dress
alone, yet it is certain that the men's was also influenced from the
same quarter. Meteren, the Flemish historian, informs us that
Count Horn had on at his execution a cloth bonnet of Milan75.
Please to turn to Quijote II, 23, and you will find the same head
—102→
gear given to Montesinos: «cubríale la cabeza una gorra milanesa
negra»
. Covarrubias minutely describes this, and it will most
properly appear in the comment. The state of Milan having been
so long under the dominion of Spain, easily accounts for this
usage.
The ancient European chivalry had many rites and customs in common, but the several states and kingdoms had divers peculiar to themselves, and totally different from one another. In England, the clergy had the power of making knights, as appears from Ingulphus76, and that the Normans abhorred this custom, and looked on those so made as dastards and degenerate. However they afterwards gave into the same, for William Rufus was knighted by Lanfranc, Archbishop of Canterbury, in the life of his father77, and his brother Henry the First granted the same privilege to the abbots of Reading, as it appears from his foundation charter. But possibly this species of church power was not peculiar to England, for Matthew of Westminster tells us that Walwanus, King of Norway, was knighted by Pope Vigilius in 533. But anciently there was ever a great intercourse betwixt knights and the clergy. The swords, arms, and banners of the former were consecrated by the clergy78. To both, fasting and abstinence from meats were alike enjoined by the Council at Avranches in 117279
. The learned Monsieur de LaCurne de Sainte-Palaye, in his Mémoires sur l'ancienne chevalerie, has amassed a number of curious particulars respecting the general institute of knighthood, and has given a succinct history of it, but it must be remembered that his work is the work of a Frenchman80. His inferences are formed and his knowledge of facts is almost, if not wholly, derived from the writers and historians of his own country, to which, and for whose —103→ use principally, he bent the whole of his pursuits. This then will by no means be found to be a proper guide for us in forming a judgment of our illustrious hero Quijote, as a Spaniard cannot with any propriety be called before a French tribunal.
Let us inquire, then, if his own country affords no laws by
which to try him. Luckily she does; and, I am afraid, by them he
will be found to be a culprit, and to have erred fundamentally.
These are Las siete partidas del sabio rey don Alfonso el nono. These
are the laws of Castille in Spanish, which were begun to be reduced
into one system by order of the king don Fernando el Santo,
and were completed in the time of his son Alfonso the Tenth,
surnamed the Wise, and made public in his name. They were
called Partidas on account of their being divided into seven volumes81;
there being seven letters in Alfonso's name, was the sole
cause of this division. These partitions, or volumes, are again
divided into several principal titles which contain the several laws.
Thus Partida II, Title 21 has no less than twenty-five respecting
knights -«de los caballeros»
- and among these the eleventh specifies
in whose hands was vested the power of making knights, and
who could not. From them we learn that they could not be created
by one who was no knight himself, that no clergyman or religious
person had this power82. I fancy Quijote's knighthood upon this
view of things is upon no better footing than Andrew's master,
Juan Haldudo's, in the fourth chapter, as the innkeeper did not
really pretend to any such honour.
Another flagrant violation occurs I, 11, where Quijote forces
Sancho to sit by him, and to eat and drink with him, telling him
that knighthood puts all upon an equality. «Ni al comer»
, says the
twenty-third [title], «non debe asentarse con ellos escudero, ni otro
ninguno, sino caballero, o ome que lo mereciese por su honra o por
su bondad»
. This title contains several curious particulars which
—104→
will greatly illustrate the history of the renowned knight of La
Mancha, and their merit will best appear when confronted with
the text.
As Cervantes was master of all the learning of his own country,
as well as that of Italy, he could not be unacquainted with this
body of laws, and wherever his hero deviates from any precepts
here laid down, it was doubtless with design to heighten the
ridicule of his character. In this however he is eccentric, though at
other times perfectly conformable. We have a notable instance of
this in a conversation of his with his squire. «Tell me»
, says he to
him, «what greater content can be had in the world, or what
pleasure can be equal to that of conquering in battle, and to that of
triumphing over one's enemy? Without doubt, not any»
(I, 18). For
knights hold it, says the nineteenth law, that no pleasure they
could have, was so good as to be conquerors83.
Let this specimen under the First Part suffice. In the second,
chapter the thirty-fourth, after the hunting the wild boar, and the
injury done his green coat, Sancho expresses his dislike to kings
and princes exposing themselves to the dangers of such chases.
The duke tells him of his error, that the exercise of hunting is more
convenient and necessary for kings and princes than for any other,
that the chase is an image of war. Let us for the present make our
farewell visit to don Alfonso, Partida 2, Title 5, «Cuál debe el rey ser
en sus obras»
, ley 20, «Cómo el rey debe ser mañoso en cazar»
. And
there we are told, «que conviene esta mucho a los reyes, más que
a otros omes. E esto por tres razones: La primera por alongar su
vida, &c. La segunda, porque la caza es arte e sabiduría de guerrear
e de vencer, de lo que deben los reyes ser mucho sabidores»
.
Much knowledge respecting the general manners of the thirteenth, in which these laws were promulged, and preceding centuries is to be derived from the perusal of them. Many of the customs continued for ages after: nay, the present king of Spain shows a more than common regard to the particular law of the chase. The Valencia edition of this work, with a copious index, was handsomely and correctly printed, in eight octavo volumes, in —105→ 1758.
But the article of knights and knighthood, which naturally gave rise to the mention of it, has been historically treated by more than one writer in Spain. The principal under this head that has come to my possession is El Doctor don Joseph Micheli Márquez, the Sicilian, in his Tesoro militar de caballería en Madrid, 1642. We have here many examples of the ancient and modern forms of arming and professing the knights, agreeable to the ceremonials of the several orders: their rules, their constitutions, privileges, and grants; their ensigns, habits, origin, and conclusion of many of them: in a word, variety of information concerning them, with difficulty elsewhere to be met with. From whence I infer that knighthood, in its various forms, participates more or less of the andante or errant, and the laying the sword on the novel knight's shoulder is nothing more than the host's gentil espaldarazo on Quijote. Whatever is mentioned in the different parts of the work on this head will be historically ascertained by corrobating passages from this and from other writers who have expressly or accidentally treated this subject, and whom it is not material to specify.
The Historia verdadera del rey don Rodrigo, por el sabio Alcaide
Albucácim Tarif Abentarique, will afford us some curious matter. We
are told by Miguel de Luna that he completed the translation of
the first part of this work from the Arabic, November 30, 1589. That
it became popular is most probable. I have this printed in quarto
en Granada, 1592. The second was published there in 1600. Both in
Zaragoza, in 1603, and in Valencia, 1606. It abounds with the
phrases and much of the diction of Cervantes, who has with great
humour ridiculed a circumstance gravely related (I, 7) of a Christian
woman taken by sentinels of the captain Tarif Abenziet, who,
on being brought into his presence, informed him that she had
heard her father read «un pronóstico, el cual decía que esta tierra
la habían de perder los cristianos, y que había de ser conquistada
de los moros. Y decía más que el capitán que la había de ganar,
—106→
había de ser valeroso y fuerte, y para señal de su conocimiento
había de tener un lunar peloso tan grande como un garbanzo sobre
el hombro de la mano derecha. Acabadas de decir estas razones por
aquella mujer, Tarif se holgó mucho, y en presencia de todos los
suyos se desnudó; y habiendo mirado con cuidado hallaron el lunar
que la mujer había dicho»
. Who can entertain a doubt that Cervantes
intended a banter on this piece of history, in what Dorotea
relates to Quijote of the prophecy of her father concerning him
who was to be her deliverer (I, 30)? He said besides that he was to
be tall in his body, dry-faced, and that on his right side under his
left shoulder, or thereabout, he was to have un lunar pardo de ciertos
cabellos a manera de cerdas, a gray mole with some hairs and bristles.
On hearing this Don Quijote said to his Squire, «Hold here, Son
Sancho, help me to strip; for I wish to see if I am the knight, that
this wise king foretold»
. «Now, why would your worship strip?»
said Dorotea. «To see if I have this mole, which your father mentioned»
,
answered Don Quijote. «You need not strip»
, said Sancho,
«for I know that your worship has a mole of these marks on the
middle of the backbone, which is a mark of a strong man»
. «This is
enough»
, said Dorotea, «for with friends we must not look upon
trifles, and whether it be in the shoulder, or on the backbone, is of
little consequence; 'tis enough that he has a mole»
.
Whatever respects the Conde don Julián and his daughter La
Cava is here delineated, and possibly from a passage respecting
the Moorish King Abilgualit (Part 2, Chap. 2), of whom it is said,
that he never eat [sic] or drank out of any vessel of gold or silver -«ni se llamaba un médico a ordenarle la comida»
- nor called a
physician to order his diet. He took the hint of Doctor Pedro Recio
de Tirteafuera, who was so troublesome to Sancho in his government.
Various illustrations are also to be derived from the Crónica del
famoso caballero Cid Ruy Díaz Campeador. The history of the horse
Babieca will better appear in an annotation than in any other
mode. The same may in a great measure be said of the traitor
Vellido, who is named in the twenty-seventh and twenty-eighth
chapters of the First Part; but as his history is blended with that of
—107→
don Diego Ordóñez de Lara, in the second, Chap. 27, it may not be
amiss to have recourse to the last-named history: and there we
read, Chap. 66, «De cómo don Diego Ordóñez hizo el riepto a los de
Zamora sobre la muerte del rey don Sancho. E respondió don Diego
Ordóñez: 'Los castellanos han perdido su señor, e matóle el traidor
de Vellido seyendo su vasallo, y vos los de Zamora acogísteislo en la
villa. E por ende digo que es traidor quien traidor tiene consigo, si
sabe de la traición e si lo consiente. E por ende riepto a los de Zamora
también al grande como al chico, e al muerto como al vivo, e así al
nacido como el que es por nacer. E riepto las aguas e riéptoles el pan e
riéptoles el vino'»
.
These circumstances Quijote mentions in his harangue to the
rebuznadores or braying party. «Hallo», says he, «según las leyes del
duelo, que estáis engañados en teneros por afrentados, porque
ningún particular puede afrentar a un pueblo entero, sino es
retándole de traidor por junto, porque ignoraba que sólo Vellido
Dolfos había cometido la traición de matar a su rey; y así retó a todos,
y a todos tocaba la venganza y la respuesta. Aunque bien es verdad
que el señor don Diego anduvo algo demasiado, y aun pasó muy
adelante de los límites del reto, porque no tenía que retar a los
muertos, a las aguas, ni a los panes, ni a los que estaban por nacer, ni a
las otras menudencias que allí se declaran»
.
In the beginning of the thirty-fourth chapter, the Duchess
makes Sancho sit by her on a low seat, and tells him that «merecía
el mismo escaño del Cid Ruy Díaz Campeador»
. The Cid seems to
have had a whimsical regard and attention to this utensil, and his
chronicler has mentioned it as often, if not oftener, than his horse
Babieca. I think I have rightly rendered the word, as will appear
from the use he made of it. «E el Cid» (says the Crónica) «había por
costumbre de comer a mesa alta en su cabo asentado en su escaño»
(Chap. 196). «E desque había comido adormecíase a las veces en el
escaño»
(Chap. 230). «Era muy noble y muy sutil de labor, e estaba
cubierto de paños de oro muy ricos»
(Chap. 248). «E el Rey dijo, 'no
sé rey en el mundo que mas merezca este escaño que el Cid mi
vasallo. E éste ganó él en Valencia'»
(Chap. 249). From this last
citation it appears that the Duchess paid Sancho no small compliment.
—108→
I know of no writer who says so much of the Caballero Sant
Yago -the Knight St. James- as the present chronicle. «Acaeció
que un obispo estando en su iglesia de Santiago, faciendo su
oración en su vigilia, oyó a los de la villa y a los romeros, que
venían ý a romería, que Santiago que apareció como caballero en las
lides, e en las ayudas de los cristianos. E cuando lo él oyó, pesóle
mucho, e dijo: 'Amigos, no le llamedes caballero, mas pescador.' E
teniendo esta porfía, plugo a Dios que se adurmió, e aparecióle
Santiago, e díjole: 'tú tienes por escarnio porque me llaman caballero,
e dices que lo non so. Por esto vine agora a ti a mostrárteme,
porque jamás non dudes en mi caballería, ca soy caballero de Jesucristo,
e ayudador de los cristianos contra los moros'. E él diciéndole
esto, fuele traído84 un caballo muy blanco, e el apóstol Santiago
cabalgó en el, muy bien guarnido de todas armas, frescas, claras y
muy hermosas a guisa de caballero»
(Chap. 14).
Now let us take a view of our knight, who, among his other
adventures, II, 58, discovered the image of the patron of Spain -de
las Españas- on horseback, his sword ensanguined, trampling on
Moors, and walking on their heads. And on seeing it, Don Quijote
said, «This indeed is a knight
-es caballero- of the squadrons of
Christ. This they call Don San Diego Matamoros, Don Saint James the
Moorkiller, one of the most valiant saints and knights that the
world ever had, and heaven now has. And many times they have
seen him visibly overturning, trampling upon, and destroying the
Moorish squadrons; and of this truth I could produce many instances,
which are related in the true Spanish histories»
. Thus far
the hero of the piece proceeds.
This saint's assistance in the battles of the Spaniards, and his services, therein are recorded in the chronicles of Spain that were composed by order of the king don Alonso [sic] el Sabio, and printed in Zamora, 1541, fol. 232. And Mariana, to humour his countrymen, tells the same story, libro 9, cap. 2; libro 12, cap. 15 & al. To these respectable testimonies may be added what Rivadeneira has advanced of this saint in his Flos sanctorum.
—109→
The above-named chronicle mentions the king don Alonso the
Sixth his ordering the palaces of Galiana to the use of the Cid for
his place of residence in Toledo, cap. 247. You will please to recollect
that Sancho, among his melancholy reveries in the pit (II, 55),
observes that his master would regard those depths and dungeons
as flowery gardens and palaces of Galiana: «tuviera estas profundidades
y mazmorras por jardines floridas, y por palacios de Galiana»
.
On having recourse to a description of this city by Doctor Francisco
de Pisa, printed there in 1617, after much being said of these, there
is this remark: «Volviendo a los palacios de Toledo, el vulgo llama
palacios de Galiana a una casa que está ya casi asolada, en la Huerta
del Rey: mas, a la verdad, aquélla era una casa de campo y recreación,
con sus baños, en la cual dicen que la misma Galiana se deleitaba»
.
Many passages concerning this city, which occur in Cervantes,
will receive illustration from this quarter. Navagero, in his
Viaggio in Ispagna85, notices this part of the city, and an ancient
palace there in ruins.
Local, poetical, and historical allusions are occasionally interspersed
through the whole work. Thus, when Quijote has finished
the adventure of the lions, II, 17, the author apostrophizes to him,
and addresses him «segundo y nuevo don Manuel de Leon, que
fue gloria y honra de los españoles caballeros»
. There is abundant
testimony of the valour of this Knight. He makes a distinguished
figure in the Civil Wars of Granada86, where much concerning his
prowess is to be read; nothing however to cause him to be here
named in preference to any other of his countrymen. That it is not
mentioned at random, but with the strictest propriety, will appear
from what is recorded of him by Alonso López de Haro in his
Nobiliario genealógico87. In the first volume, p. 200, he tells us that he
—110→
was called «el valiente, honra y gloria de la nación española»
. In
the second, he relates, p. 118, the following piece of history, altogether
pertinent to this of Cervantes. «Fue de los caballeros cortesanos
en gala y bizarría, que se hallaban en la corte deste católico
príncipe, del cual escriben que habiéndole traído de África un
presente de leones muy bravos, con quien las damas de la reina se
entretenían, mirando desde un corredor que salía a la parte donde
estaban los leones, en cuyo sitio se hallaba don Manuel88. A este
tiempo sucedió que la dama a quien servía, por descuido o por
bizarría dejó caer un guante en la leonera, dando muestras de queja
de habérsele caído, y como don Manuel lo oyese, abrió la puerta de la
leonera con mucha presteza, entró dentro con grande ánimo y valor
donde los leones estaban, sacando al guante y llevándole a la
dama»
. This truly quixotic action of don Manuel attracted the
encomiums of the Spanish poets Garci Sánchez de Badajoz (as it is
related by de Haro, who also adds that the historians are large in
their accounts of this famous and celebrated captain) and don
Jerónimo de Urrea, who commemorates this act in a stanza which
he has inserted in his translation of the Orlando furioso into Spanish.
From tome the first of de Haro's above recited work, p. 422, we learn that Pedro Rodríguez de Luna [sic] was the author of a book, Del paso honroso de Suero de Quiñones, whose jousts there were mentioned by Quijote, I, 49. A farther account of them is to be had from the Crónica de don Juan el Segundo, to whom must be added Zurita, and they will be elucidated in the notes. Much is said by de Haro of the Marqués de Santa Cruz don Álvaro de Bazán (see parte I, cap. 39), and he enumerates several facts which tally with Cervantes his account of the battle of Lepanto.
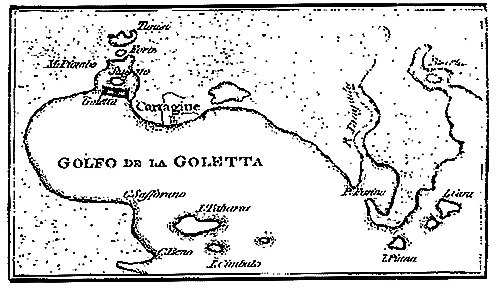
The affairs of Tunis and the Goleta are lightly touched here; for a fuller account of these recourse must be had to Italy. There is a small quarto volume on this place, and (what is remarkable) —111→ printed the very year our Author mentions: Discorso della Goletta, et del Forte di Tunisi, con quello che può forse succedere, quando il Turco tenti tale impresa89. In the title of this rare little tract is a small map, in which are delineated the Goleta with its gulf, the pequeño fuerte o torre en mitad del estaño, Tunis and its Fort.
As words convey but poorly the idea of a place, I have sketched this little map, and here inserted it.
If the island situated opposite C. Bono be I. Cimbalo, as seems probable, then from the authority of Luis del Mármol, I can pronounce the long island under C. Saffarano to be Tabarca, mentioned by Cervantes, I, 39.
The round spot in the stagno, or lake, is the little fort, or, as the
Italian expresses it, «la Goletta Vecchia, Piazza non molto grande»
90.
Cervantes speaks of Gabrio Cerbellon as general of the fort: this
possibly, as it was situated between the walls of Tunis and the lake,
as appears from this writer, and the plan was an appendage to the
government of the city of Tunis, of which we here learn he was left
General by Don John of Austria, which is also confirmed by other
authority. «L'anno 1572, Gabrio Sorbellone91 da S. M. fu fatto Vice-Re e Capitan Generale di Tunisi di Barbaria, e de suoi supremi
concigli, avendo poi gli Turchi con poderosa armata presa la
Goleta, dove fu anche tradimento, assediorno con forze immense
—112→
la nova fortezza fatta erger in qual regno di Tunisi, ma non terminata
dal Vice Re, che trovandosi en essa valorosamente ributto el
nemico, sostenendo quattordici assalti generali92, e finalmente per
breccia di due mine presero i Turchi a viva forza la piazza con un
essercito innumerabile, restando prigione il medesimo Capitane
Generale, che fu condotto in Constantinopla»
. He died in Milan, in
January 158093.
It is not my intention at present to trouble you with any extracts from that great ornament to his country Mariana, though he has several passages for our purpose. As his history has afforded me much information and satisfaction in the perusal, give me leave to add to the just elegies of it by Padre Feijoo94 this testimony: that though a Spaniard, he held rational, manly notions of liberty, and though a Jesuit, he has all the appearance of candour and honesty.
There were several lesser incidents in his own time to which
Cervantes alludes, the knowledge of which can be no otherwise
had than from his contemporary writers, or those who soon came
after him. An instance or two will suffice. In a conversation between
Quijote and Sancho concerning relics, the master says, that
kings carry the bodies of saints, or their relics upon their shoulders:
«Los cuerpos de los santos o sus reliquias llevan los reyes sobre sus
hombros»
(II, 26). Of this custom we have two examples in the Flos
sanctorum of Rivadeneira. The first, that of the reception of the
relics of Saint Eugenius at Toledo, in the year 1565, in which «entre
muchas cosas señaladas»
, that writer tells us, «la más insigne fue
ver al católico rey don Felipe, y al príncipe don Carlos su hijo, y a
los archiduques de Austria Rodolfo, que hoy es emperador, y
Arnesto su hermano llevar sobre sus hombros el arca en que iba el
—113→
cuerpo del santo Pontífice95»
. The other was also in the same city
when the same king and his son paid the same devoirs to the
Patroness of it, Santa Leocadia: «llevaron sobre sus hombros el cuerpo
de la Santa Virgen»
96. This was in the year 1586.
Though the expulsion of the Moors from Spain is sufficiently
notorious, yet the particular allusions to the conditions of the bando
or proclamation are not so. In the course of the morisco Ricote's
conversation with Sancho, he desires his assistance to carry away
the treasure which he had buried and left behind him when he
was forced to quit Spain, which Sancho refuses, but promises not
to discover him. «'Mira si quieres venir conmigo, como te he dicho,
a ayudarme a sacar el tesoro que dejé escondido'. 'Ya te he dicho,
Ricote,' replicó Sancho, 'que no quiero. Concéntrate, que por mí no
serás descubierto'»
(II, 54). Honest Sancho detested the office of
informer, and overlooked that part of the Royal Mandate: «Que
cualquiera de los moriscos que escondiere o enterrare ninguna de la
hacienda que tuviere por no la poder llevar consigo incurran en la
pena de muerte los vecinos del lugar, donde esto sucediere97»
. This
condition extended to the persons of the moriscos, and the ninth
mandate directs as follows: «Mandamos que ninguno del presente
reino sea osado de ocultar ni encubrir en sus casas, ni fuera dellas,
a cualquier persona o personas de los dichos moriscos, así hombres
como mujeres, niños o niñas, de cualquier edad y condición que
sean»
. This is the mandate to which Sancho refers in his discourse
to Ricote concerning his daughter a few lines after those cited,
where he tells him: «Muchos tuvieron deseo de extenderla y salir a
quitársela en el camino, pero el miedo de ir contra el mandado del
Rey los detuvo»
(II, 54).
There is but one writer more that I shall at present mention, —114→ and to be silent respecting him would be impious. Pium est profiteri per quem profeceris. What critical reader is there of Shakespeare, who would not rather wish to consult a good dictionary of our Language, if any such existed, compiled in his time, than all the labours of almost any editor without it? What in this instance is in vain to be wished for, I have the good luck to possess with respect to Cervantes in the Tesoro de la lengua castellana o española, por don Sebastián de Covarrubias Orozco, 2 tomos, en Madrid, 1674. I have not only occasionally consulted and carefully read through the whole of this work, but have also transcribed whatever appeared proper to illustrate and to be confronted with the text, and am very clear that here only are to be found the true import and meaning of many parts of Cervantes's phraseology.
There are two editions of this book: the first in Madrid, in 1611, and the fore-mentioned Baretti's account of it, and of Spanish literature [in] general, is egregiously defective and erroneous. Father Noydens seems to have been the editor, and if he showed any judgment, it was that of adding to it the learned Aldrete's Origen de la lengua castellana, which was first published in Rome in 1606. But his own additions are trifling, insignificant, and of very little or no worth. Covarrubias laid the foundation of that superstructure that was afterwards with good judgment completed by the Spanish academicians in their Dictionary. They own their obligations and pay all due deference to his merit in the Prólogo to their voluminous work, and in their history of their Academia.
But the Tesoro is not a dictionary of words alone. It abounds in history, local and personal, and accounts of its national customs are scattered throughout the whole work, and will be made use of where necessary. I shall content myself with one at present, which is furnished from Thomas Cecial's nose, which, besides being full of warts, was also de color amoratado, como de berenjena98. Covarrubias observes that he who is much used to the eating of berenjenas, besides other mischiefs, its bad quality shows itself in the face by giving it a livid and dark green colour. The reading the whole —115→ work became necessary, as will also appear in many places in the annotations, from many irregularities in the alphabetical arrangement of the whole, which I have reason to think was the cause of some omissions in the great Dictionary99.
In this latter a meaning is assigned to the words of Cervantes from his use of them; the former gives us the sense as it was in his time. It requires no nicety to distinguish which of the two is right.
Thus, Sir, without launching into what Quijote calls the mare magnum of his histories, the libros de caballerías, I have given you a specimen of what may be done towards illustrating this great author, but from this source much is to be derived, as it is clear that it was his intention as much as might be to copy their very language, imitando en cuanto podía su lenguaje. Numerous examples under this head I have selected, and where the same were to be found in many books of this kind, many have been rejected.
That Cervantes was himself the original Quijote as to the article of reading, that there was a time, perhaps a long period, when with the undistinguishing multitude of his countrymen he perused these with great pleasure and satisfaction, and impregnated his memory with their respective subjects and singularities, seems unquestionable from the use he made of them. That he was minutely attentive in his reading them has every appearance of probability from this circumstance: that speaking of Gasabal, the Esquire of Galaor, he observes that his name is only once mentioned in the history of Amadís de Gaula. Apprized of this, on perusing the four books I found it to be a fact: he is only mentioned, Libro 2, Cap. 59, and is spoken of in two other places, but is only there named.
The genuine text of authors of super-eminent abilities has ever, with good reason, attracted the attention of the curious. Much of this has of late been given to that of our countryman Shakespeare, who has no competitor in the article of great original genius, but —116→ his illustrious contemporary Cervantes. If the Giunta edition of the Decamerone of Boccaccio has been ever so generally esteemed as to have been more than once with great niceness counterfeited, if its acknowledged reputation raised the surprise of Paolo Rolli that the other editors had not reprinted to a tittle this edition, and that they had preferred the frivolous vanity of their own orthography, or their caprice in the form of the book, to the just liking of the lovers of this work, his edition ought therefore to be so much more gratefully received, as being a re-impression of the true and most approved text, page by page and line by line, with the same orthography and punctuation100. It may be hoped, therefore, that an edition of Don Quijote, executed with equal fidelity in this particular, with others of much apparent utility, which will in due time be specified, may prove equally acceptable. To this end, the first editions must be selected for that purpose.
The only one of modern times that merits any kind of notice is
the pompous London edition, a work that reflects great honour on
its noble patron101. Upon a careful collation of its text with the first,
it may be pronounced to be in the general pretty exact. The errors,
however, of the original are carefully retained, and such they are,
if we had an opportunity to consult the manuscript of the author,
and should find them in his own writing. Pineda in that book
which he puffed off and published, Fortuna de amor, por Antonio
de lo Frasso, took care to inform us that it was he that «revised,
—117→
amended, put in good order, and corrected the London edition of
Don Quijote»
, a business for which he appears to have been every
way unqualified, as will appear in the sequel. It must be observed
that in his editorial capacity he acted in some degree with the
punctuality of a Hearne102, but not with his openness, who, when he
inserted anything notoriously wrong, took care to apprize his
reader of it. Let the following suffice: «Con la batalla que el valiente
Detriante hizo con el alano»
(I, 6); it stands thus in the first and in
every other edition. The true reading is undoubtedly «con la
batalla que el valiente de Tirante hizo con el alano»
. The title of the
fifty-ninth chapter of the history of Tirante is «Como Tirante se
combatió con un alano &c.»
This brings the fact home to him. As to
the rest, it is to be observed that there is nothing more than a
transposition of the letters103. The particular diction of «valiente de
Tirante»
is a Spanish idiom. The de is redundant, so we read, I, 36,
«El bueno de Sancho»
, and I, 50, «a este pobre de Sancho»
. So in the
above chapter of Tirante: «El pobre de Tirante tenía muchas llagas»
.
A similar error uniformly handed down to us: «puso piernas al
castillo de su buena mula»
(I, 8), read costilla the rib.
As I have minutely and critically collated the first editions of the first and second parts of the years 1605, and 1615, as well as that of 1738, and have noted down their errata, and deviations the one from the other, though I before advanced that the errors of the original are retained, yet have I no reason to suppose the former were always made use of in the publication of the latter: if they were, I have only to add, it was to no good purpose, as will more clearly appear if the notes and collations should see the light. There are several others of the like kind with the above-named, which it is needless at present to point out. Thus much for Pineda in his office as reviser.
Of himself he added various other errors, and with the true
spirit of a critic by profession, perverted and obscured what was
easy, clear, and perspicuous, amended and corrected much for the
worse. The following passage, as it stands in the edition of 1615, II,
—118→
1, will corroborate what is here asserted. «Mas agora ya triunfa la
pereza de la diligencia, la ociosidad del trabajo, el vicio de la virtud,
la arrogancia de la valentía, y la teórica de la practica de las armas»
.
With the absurd punctuation of Pineda's text 'tis hardly intelligible:
«la pereza, de la diligencia, la ociosidad, del trabajo, el vicio, de
la virtud, la arrogancia, de la valentía, y la teórica, &c.»
This instance
is not single104, but it is needless to enlarge.
But he has taken greater liberty, and foisted in his own readings
without any authority. Hence we read, II, Prólogo, «función
prodigiosa»
for «facción prodigiosa»
. So II, 17, «replicóle el hidalgo»
,
while the original is «respondióle»
. «'Ahora, señor,' dijo don
Quijote»
or «replicóle105 don Quijote». So again II, 49: «Hola, assidle,
y llevadle», while the original is: «assilde hola, y llevadle»
.
If an
editor takes these unwarrantable liberties of altering the text to his
own whim, how shall the reader know whether the text before
him be genuine or not?
In what follows it will appear that by his omission of one
important word, and by his corrupt and ill-judged reading, he has
mutilated and quite spoiled the passage (II, 62): «En comenzando
el paseo, llevaba el rétulo los ojos de cuantos venían a verle, y
leían: 'Éste es don Quijote de la Mancha'. Admirábase don Quijote
de ver, &c.»
As it stands, and should stand, in the original it is as
follows: «y como leían: 'Éste es D. Q. de la M'. admirábase D. Q.»
«In beginning the walk, the inscription drew the eyes of as many
as came to see him, and as they read 'This is Don Quijote de la
Mancha,' Don Quijote was in astonishment himself to see, &c.»
The reading the inscription and, in consequence of it, naming and
knowing him, was the source of the Knight's astonishment, and
nothing can be more flat, insipid, and unmeaning, than that they
only read it.
How far his arrangement and disposition of the whole was judicious, how far it is to be admitted that he has put the work into good order, will appear from a survey of what he has done, and an inspection into the first editions. If he had made a proper use of them, he never would have given that title that he has done, viz.
—119→«VIDA y Hechos del ingenioso Hidalgo D. Q. The life and actions of the witty gentleman D. Q.» You need not be told that the commencement of the history is not till about his fiftieth year, and that nothing is recorded of him till that period, but his general character. The time of action in which the hero is employed is not quite so obvious, but it is certain it did not exceed ten years. This is to be inferred from the age of the ama, or housekeeper, who at first being named is said to be turned of forty, and who, to enforce her arguments to dissuade her master from turning shepherd at the beginning of his last illness, mentions her being turned of fifty. The Vida then cannot with any propriety be retained, as the history does not contain more than the sixth part of it.
In the plain title of the first edition, the hero of the book is called «El ingenioso hidalgo don Quijote de la Mancha. Compuesto por Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra. Dirigido, &c. Año 1605. En Madrid, por Juan de la Cuesta». This was divided by the author into four parts, but the chapters, in number fifty-two, are in one sequence. So are those of the second, but the division of that into parts or books, is not to be found there. The Tabla de los capítulos in both is at the end.
Whatever proceeds from the pen of a Cervantes is not to be thrown by as useless, or without good cause to be rejected, which has been the case with the Dedications of both parts. To that of the former to the Duque de Béjar, there is a direct allusion in the Versos de Urganda. The second is a facetious grateful address to his other beneficent patron Don Pedro Fernández de Castro, Conde de Lemos, and is undeservedly consigned to oblivion. The licences, approbations, and censures should be also retained, as they contain many curious particulars respecting the history of the work itself not elsewhere to be had.
As there elapsed ten years betwixt the publication of the first
and second parts, it might have been expected that the author
should have removed such of the errors of the former part as
concerned himself, such as his placing Sancho on his beast in the
same chapter just after Ginés de Pasamonte had stolen it, and the
misnomer of his wife, whom in the seventh chapter he names
Juana Gutiérrez, and a very few lines after, Mari. In the fiftysecond
chapter, he calls her Juana Panza, «que así se llamaba»
.
—120→
Here again, the text is arbitrarily altered without any notice to the
reader of the change. Teresa is substituted without any authority.
Blundering about words and actions is not a more essential
part of Sancho's character than his happy memory, of which the
history affords several facetious instances. «La memoria»
, says he,
I, 25, «tengo tan mala que muchas veces se me olvida cómo me
llamo»
. Some excuse this for his calling his wife Teresa, as he does
everywhere in the second part. A notable transaction of this kind
offers in the next chapter, with his master's letter to Dulcinea,
which affords much pleasure to the curate and the barber.
Uniformity of character is the truest test of genius, and poetical merit. Sancho's in particular
|
So II, 43. He tells his master that he neither does nor shall any
more remember his counsels, than the last year's clouds: «no se me
acuerda, ni acordara más de[l]los, que de las nubes de antaño»
(II,
44). Accordingly, though he receives them in writing, II, 44, he
drops them, and they come to the hands of the Duke and Duchess.
Enough has been said under this head in some degree to
excuse the author. When the counter-Quijote Sansón Carrasco is
first introduced, Sancho speaks of him as the son of Bartolomé
Carrasco (II, 2). But forgetting himself in another place (II, 28), he
makes Thomas Carrasco the father of the Batchelor. I will not take
on me to assert that these errors were originally designed, but
certainly they are altogether characteristic in the mouth of the
person who utters them. As Sancho's Rucio, less renowned than
Rocinante, had led the author into a great mistake, he has with
propriety ingenuously admitted the same by putting it into the
mouth of his master: that either the historian was deceived, or that
—121→
it was the carelessness of the printer. In the fourth chapter of the
second part he has supplied some defects in the former, turned
commentator on himself, and pointed out the use he made of his
reading by his alluding to the fact of the noted thief Brunello's
stealing Sacripante's horse at the siege of Albracca, which was first
of all largely related by Boiardo, and afterwards introduced with
additions by his happy continuator Ariosto; and these will be
inserted in their proper places among my annotations.
These two illustrious bards, of whom Italy may justly boast, seem to have been our author's favourites, particularly the latter. The famed helmet of Mambrino, the property of Rinaldo, and the great object of our knight's esteem, makes a figure in both. A careful perusal of these, which has given me much pleasure (I wish I could say the same with truth of many others!), and has furnished from the former more than forty elucidations of the text; from the latter perhaps more than double, as there are indisputably many allusions directly pointed to several passages in the Orlando furioso, particularly to his armour (I, 13; II, 66), to the discord in Agramante's camp (I, 45), with many other lesser incidents, which have cost me no small pains to point out. Such are those mentioned I, 25, of the mad knight's pranks, all of which are specified from the original, and in the same chapter the Hipogrifo of Astolfo, and the renowned Frontino. 'Twas certainly a slip of memory in Cervantes to make Medoro the page of Agramant, which he does I, 26. Dardinello was his master, as appears from Ariosto, in the eighteenth chapter, where he first makes his appearance, stanza 165.
|
Nor do I find him any where connected with Agramante. Such trifles as these are at once to be pardoned and passed over, were it only to comply with the good-natured dictates of Horace
—122→
|
Many variations in the text necessarily present themselves. The most striking are those in the First Part (for these are unquestionably but two, Cervantes, in the title of the Second, styling himself autor de su primera parte) where, at the end of the eighth and beginning of the ninth, and so on, in Pineda's division of the whole into books, the word libro is substituted for parte. I do not believe he was the first who made this change. The numbering of the chapters in both is one, no notice being taken of the division. In the second, as there was none primarily, so is there no foundation for any distinction of it into books.
As it is my ultimate wish to have the text pure and genuine, I would spare no pains to effect this. For which purpose the first, printed in Madrid 1605, in quarto, by Juan de la Cuesta, seems to permit the preference. This I have very carefully collated, as I have also that of the second part by the same printer. But there is also another edition of the first part the same year and place, and there were two more, one in Lisbon, in 4to, and in Valencia, in 8vo, the first year of its appearance. These three last have never yet come to my inspection, nor that of Madrid three years after, in 1608, in 4to. These, and any subsequent edition in the life of the author, I should be glad to peruse. As to the second part we have no choice, as there is no reason to apprehend that it underwent more than one impression in the life of the author, which is farther confirmed from this circumstance, that no privilege is specified for the printing it in Aragon and Portugal, as is the case in the first of 1605108, and —123→ it is also certain from the dates of the licenses, that it was not published earlier than November 1615, and he died the twentythird day of April, the same nominal day as his illustrious contemporary our countryman Shakespeare, who of course survived him but ten days109. What age ever produced two such! Take them for all in all, we never shall see their like again.
The style of Cervantes merits every encomium. It may be
compared to the noblest river, that now rapid runs with proper
velocity, now gently glides along, and suffers its crystal current to
be tinged with hues, which it receives from the lesser streams that
mingle with its waters. To drop the allusion, the language of Don
Quijote, tho' the purest and most elegant of the Castilian, has its
variations and inequalities, conformable to the persons in whose
mouths it is put and to the subjects treated of. The character of the
Biscayan is most truly drawn, and with his own confused notions
of things he speaks of himself in the absurd idiom of his own
country, in the second person: «Así te matas, como estás ahí vizcaíno»
.
The angry knight, in the violence of his resentment against
Sancho, speaks a leash of languages at once, and styles him gañán,
faquín, belitre110. It has this in common with ours in Hudibras, that
many vulgarisms are here and there scattered throughout the
whole, which are seldom used by writers, but frequently in conversation.
Many of these in our author are collected together by
Quevedo in his Cuento de cuentos, and are styled vulgaridades rústicas.
Such as the following: manos a la obra, quítame allá esas pajas,
hombre de pelo en pecho, and many others of the like sort, which, as
occasion offers, will be pointed out.
But there is no end to his proverbial diction. He sets out with
—124→
it, and where there seemed to be no reason to expect it there I have
discovered it, so that I may make use of one of Sancho's, and apply
it to this purpose: «donde no piensa salta la liebre»
(II, 10). «Una
olla de algo más vaca que carnero»
is certainly of this kind. «Dice
un proverbio: 'Vaca y carnero, olla de caballero'.»
This is quoted by
Covarrubias. In conformity to a direction of this kind, Carrasco's
squire, Thomas Cecial, acted when he treated his brother Sancho:
«volvió con una gran bota de vino que traía pendiente del arzón de
su caballo»
(II, 13). «No vayas sin bota camino»
, was an old adage,
«y cuando fueres no la lleves sin vino»
111.
The explanation of the text is the principal aim of the annotations,
and they will serve not only to enumerate many places in
history, whether of the real or ideal kind. (I say many, not all, for
I stumble in my outset, and in all my searches have discovered
nothing of Gonela, and his horse who tantum pellis & ossa fuit)112.
Many customs peculiar to the Spanish nation, mentioned by our
author, will appear from the evidence of other writers, and whatever
tends to facilitate the acquisition of an acquaintance with the
Spanish phraseology and idioms must be of great utility. Betwixt
this and the Italian a correspondence will be pointed out, both
languages having some phrases in common with each other.
Though the Florentine and Castilian dictions are in many respects
equally pompous, yet I cannot but subscribe to the testimony of
don Gregorio Mayáns of his own, that it is superior to any other in
the magnificence of its expressions113. 'Tis this that distinguishes it
from any other European tongue. «Lo majestuoso de las voces le
da gravedad y peso»
; «the majestic of the expressions gives to it
gravity and weight»
114. 'Twas this that induced Cardinal Bentivoglio,
in one of his letters to Toby Matthews, to give a singular opinion
—125→
of it. «Son valente uomini veramente gli spagnuoli nelle composizioni
spirituali, e non so come la lingua ancora porta con se maggior
peso con la sua gravita per imprimer le cose»
115.
But to take leave of the text for the present, in the revisal of it several matters are to be considered, and what other editors have done may be worth attending to. And here the state of the language when the author wrote must be duly weighted and given, not agreeable to modern refinements, but exactly as it may be supposed to have originally fell from the pen. If the author was in fault, let him be blamed. If alterations are once admitted without unanswerable objections to them, there will be no end of alterations.
I did not, in my first notions of this matter, by any means
propose to myself Nicola Francesco Haym as a pattern, but looking
casually into his address «Al lettore» in the elegant edition of the
Gerusalemme liberata of Tasso by Tonson, it gives me pleasure to
find that my plan is conformable to his as to the selection of the
first edition being the ground-work of a subsequent one. «Ho usate
tale diligenze»
: I have taken the same pains in collating. In a word,
I hope I shall be excused if I make use of a long quotation from
him, as it expresses my own sentiments and intentions.
«Ho giudicato a proposito di seguire la medesima ortografia di prima, senza farvi alcuna alterazione; e con tanta osservanza, che vi ho fin lasciato quelle incostanze che vi erano; trovandovisi alcuna volte notato, cavagliero e cavaliero, e così parimente herme e erme, heremita suo derivato ad eremita, e molte altre simili; non perché io stimi lodevole questo vacillante modo di scrivere, o perché io sprezzi la moderna ortografia, seguita presentemente da' più gran letterati d'Italia; ma perché con l'incostanze si comprova ciò che nella vita del Tasso dice il marchese Manso, cioè che il detto poema fosse in più volte —126→ stato pubblicato, e che a lui fosse interdetta la revisione delle sue opere tanto da lui desiderata; cosa in vero troppo crudele. In oltre, non potrò cosi facendo esser tacciato dessermi presa troppa libertà, ne potrò esser ripreso di averla cosi lasciata, mentre non pretendo ad altro che a darne una copia esatta, se non in quei luoghi che come si e detto, gli errori formavano un altro senso, e ch'era necessarissimo di cangiavli. Chi è quello, che non istimi più una pittura di Raffaele o di Tiziano intatta, benché in alcuni luoghi non finita o incorretta, che se in que' stessi luoghi fosse stata corretta o finita da un altro, benché valentissim' uomo? Se dunque tanto si stimano le opere de' gran pittori quando restano intatte, come uscirono appunto dalle lor mani, perché non deve aversi il medesimo riguardo per i scrittore?»116 |
To apply this to our purpose, it will hardly be denied that most languages undergo some changes in their orthography or spelling in the course of a century or two in their approach to a state of maturity. This was the case of Cervantes, who found his native tongue in that state which preceded its meridian, to which it seems he was destined to bring it.
—127→
As he retained many antiquated words, he did the same with
its orthography also. Thus we read «sin el hornato de prólogo»
(I,
prólogo); «el sentido del holfato»
(I, 20); «y haspado hilo»
(II, 28);
«ha entender»
(II, 27); «hallá te avengas»
(II, 57); «con las hancas de»
(II, 58). In the old Spanish, the h is frequently redundant. «Fueron
lo ha buscar, y él s'escondía»
(Espinosa C. 27. St. 112.) «Los pechos
y el hombligo travessava»
(ibid., C. 31. St. 43). «Cudicia rompe el
saco»
(Don Quijote, I, 20). In Luis Barahona de Soto, we read «A la
crueldad levantan la cubdicia»
(C. 9. St. 33), «Buscando su tesoro el
cudicioso»
, ib.).
I will instance but one more example on this dry subject, which is C. 12. St. 65. The word monesterio, which is notoriously wrong when compared with its origin, but which is so written in the old writers, and by the critical Covarrubias. Custom in most languages sometimes gets the better, and can hardly be set aside without affectation. These which are here produced may serve to confirm an observation of the learned Monsieur de S. Palaye, that such instances should teach the most knowing editors that they always hazard much in changing the text of authors without necessity, and without precaution. They ought at least to present them such as they have read them, with the most scrupulous fidelity; they may afterwards more hardily propose their own conjectures117. He must be very ignorant of the Castilian who wants to be informed, that it abhors the use of double consonants; thus Apollo is always Apolo, Palladium, Paladión, Pallas, Palas, &c. When this rule was finally settled, 'tis not quite certain; in our author's time, it was not. I have found the s redundant in the spelling of Luis Barahona de Soto in his Poem of Angélica in these words -confussión, ossa, osso, pissada, dessiertas, and several others. Whether this came from the author or composer of the press, custom must be some plea of excuse for the same in Cervantes.
But the text being duly settled agreeable to the original editions,
—128→
the placing the notes and commentary will come of course
to be next of all considered. And here I must in some degree plead
an exclusive power of doing this by virtue of my index -«y dejadme
a mí el cargo de poner las anotaciones y acotaciones»
. It must
frequently happen that a writer must use one word in a very
different sense; an explanation then of the same may be totally
useless in one, and altogether pertinent in another. To give a clear
idea of what is here advanced, let us take the word altibajos, which
is used in three places by Cervantes: «No ay historia humana en el
mundo, que no tenga sus altibajos»
(II, 3). «There is no human
history in the world that has not its ups and downs»
(probably an
allusion to Sancho's capering in the blanket, which produces the
reflexion), its inequalities. «Altibajo»
, says Covarrubias, «se toma
algunas veces por la desigualdad que el hombre inconstante y
vario suele tener en sus acciones y modo de proceder»
. In the two
other places, II, 19 and II, 26, the original meaning -«el golpe que
se da derecho de la cabeza a los pies»
- is retained, in the former
the metaphorical.
It has frequently happened in my searches, that one quotation has pertinently explained two distant passages. Thanks to my first labour of the indexes, this has been effected at my leisure in a few minutes. Without them much time might have been expended to no purpose, as the search might have proved unsuccessful, though there were a full and clear conviction that such a correspondence did exist somewhere, but which there was no possibility of turning to.
In confirmation of what is here observed, take the following
annotation on una villana de Sayago to which Dulcinea was changed
(II, 32). «Saco es una vestidura vil de que usan los serranos y gente
muy bárbara, Lat. sagum, que vale lo mesmo que sayal, por ser la
tela de que se hace el saco. En tierra de Zamora hay cierta gente
que llaman sayagueses118 y al territorio, tierra de sayago, por vestirse
desta tela vasta»
. I should have been much obliged to Covarrubias,
if he had made me as well acquainted with the yangüeses, as he has
—129→
with these, and with several customs of his country that fall within
the time of my enquiries.
It will be proper to say something of the indexes and the
annexed specimens. Those which contain the names of men,
countries, cities, &c. &c., must be of general utility for several
purposes, and particularly for referring to preceding passages.
Thus the author (II, 8) tells his readers that the adventures of the
hero in his third sally, begin in the way to Toboso, as the former
did in the plains of Montiel. I will suppose that many of his readers,
regardless of his directions to forget the past adventures of the
Knight -«se les olviden las pasadas caballerías de el ingenioso
hidalgo»
- to have actually done so, but wish to turn to the particular
passage; this then by the index may be done in a minute.
Allusions to past facts occur in almost every chapter, nay sometimes
in several places in one and the same, particularly the promise
of the island, which was a part of the original plan, in the
seventh chapter of the first part.
But the references which everywhere abound, and which for the purpose of profitable reading can hardly be obtained but by the aid of the indexes, must be a necessary part of the editorial labours; but this is not to be effected by these only, but by frequent reading. This more immediately respects lesser matters; the names of men and places may be very easily turned to, and discovered without any labourious search. A proper selection from the Indexes de palabras in such a manner as to discover the concording passages, the remarkable facts, and the principal transactions throughout the whole of the work, cannot fail to be of use in assisting the diligent, the careful and attentive reader.
As my aim and intentions, from uncommon labour and perseverance in the whole of this undertaking, are to display the merits, to elucidate a writer who of all the moderns has attracted the most general estimation, and who, the more he is known, must be more generally the object of admiration, whether we consider the wonderful extent of his genius (of which luckily no one was ever a more competent judge than himself, by his having set due bounds to it, as is apparent from his happy conclusion of the —130→ history), or the pleasing facetious manner in which he has conveyed to mankind those excellent lessons of morality, so I must observe, that the indexes of the proper names will admit of no curtailing or abridgment, for under the names of the knight or squire, their principal actions are pointed out. The same is done with respect to every other person, place, river, or other notable particular, nor amidst these are Rocinante's feats left unrecorded, nor his intimacy with Sancho's Rucio.
The man who is at the pains of making indexes, says the Bishop of Bristol in the preface to his Milton, is really to be pitied; but of their great utility there is no need to say anything. I can from experience bear testimony to the former part of what is here advanced. He must be steeled with seven-fold patience, and endued with a still larger portion of perseverance, who finishes what he begins in a work of this kind, and without that happy period, he is wasting time and labour to no purpose. Duly impressed with this truth, that the sole worth of the whole depended on the finishing what I had began, I used art and stratagem to impel myself on the completion of that, which, had it been proposed to me against my inclinations, I should have resisted with my utmost efforts. But my love and veneration for this author, whose every new reading still brings new pleasure, and discovers latent beauties that have eluded my former surveys, induced me to undertake that for him, which the editors of the Dauphin Classics did in their several departments under the auspices and patronage of the Duke of Montausier.
If my patience in this undertaking was many times fatigued by an uncommon exercise of it, another still more painful, namely that of reading, has at times quite overpowered it. To read over bulky volumes where there is scarce anything to instruct or amuse, which is for the most part the case of the libros de caballerías or romances, and many of them printed with types scarce legible, with numerous inconveniences to be encountered in travelling through these forests and enchantments drear, must quell the best —131→ formed resolutions. If the four first books of Amadís de Gaula, Tirante el Blanco among the Spaniards, Boiardo and Ariosto among the Italians, have furnished out some amusement independent of my searches, Felixmarte of Hircania, Palmerín de Oliva, Maestro Elizabat with his Sergas de Esplandián, I was about to add Pulci in his Morgante maggiore, but surely Alamanni in his Girone il Cortese, have in many places overpowered mine. Nothing could have urged me on to the perusal of such writers, but the view of tracing out the knight in his pursuits, and success has in many instances attended my endeavours.
I should never have engaged in the reading of these books but with a view to the present purpose, as it is with me most certain that, if a greater genius than Cervantes had arisen and exerted his talents in defence of them by a greater fund of irony, they would inevitably have sunk into the darkest oblivion, and been left to perish with the detestable Avellaneda and the poor poet Antonio de lo Frasso. What but the rarity of the Fortuna de amor could induce Pineda to reprint tan disparatado libro, and to induce him to think Cervantes in earnest in his high-strained commendations? He seems rather to have made him the butt of his ridicule, and to have treated him as a second Querno119. In his Viaje del Parnaso, a poem of very singular merit, to appease the turbulent waves betwixt Scylla and Charybdis, he is for throwing him overboard, but he is saved by the interposition of Mercury.
| Cap. tercero. | ||
—132→
Don Nicolás Antonio, forming his judgment of him from hence, styles him Poeta infi ni subselii. The painful labour of reading these sort of authors is the commentator's merit, as it is ever a great advantage that some one should take such pains for the information of others120.
When the text of the author selected for illustration is imprinted in the memory, so that the resembling passages may be brought together, the comment may go on with success; without it the allusions cannot be brought to light. An undertaking of this kind must be a work of time, and cannot by any means be completed in haste, for many very obvious reasons. But one thing more offers. As some of the editors of the Dauphin Classics adorned their works with ideal maps of the travels of their heroes, so our knight's adventures being all within the limits of his own country, a map of Spain, adapted to his history, must be not barely an ornament, but of apparent utility, as there are more than a hundred names of provinces, cities, mountains, rivers, and the like mentioned in it. Such a one, executed with proper references to the parts of the work where they are named, seems to offer a large fund of amusement. But it will be in vain to look for the Duke's territories, or the famous island of Barataria in the present attempt, which is so ordered as to serve every book, whether original or translated.
As to the idea of a future edition, the originals before-mentioned being to serve as the ground-work of the superstructure, it is to be observed, the text will necessarily be included in two —133→ tomes; the comment, with the various readings and index, would make two more. A genuine and correct text, which I have never yet met with in any modern (for several, for more than a century past, have been mutilated and expurgated), would be my chief and principal aim. Nor would I be negligent in attention to the beauty of the impression; this should correspond to the former, though it be a secondary consideration. To publish new and correct editions of the works of approved authors, says the Bishop of Bristol, has ever been esteemed a service to learning, and an employment worthy of men of learning. It is not material whether the author is ancient or modern.
If chastity of manners be any test of approbation, Cervantes
must be ever esteemed. He has in his great work proved the truth
of his own observation, «Si el poeta fuere casto en sus costumbres,
lo será también en sus versos; la pluma es lengua del alma»
(II, 16).
In a word, I must bear testimony to his own observation of his
history, that it has not an immoral expression, nor any sentiment
but what it is Catholic: «porque en toda ella no se descubre, ni por
semejas, una palabra deshonesta, ni un pensamiento menos que
católico»
. A satisfaction this, that I have not employed my time on
a work unworthy of notice.
The true characteristic of ignorance and ill-nature is to decry
and undervalue the labours of any man where they tend to any
useful purpose. I shall apply to my own intentions what your
friend Mr. Warton has said of Shakespeare: «If Cervantes is worth
reading, he is worth explaining; and the researches used for so
valuable and elegant a purpose, merit the thanks of genius and
candour, not the satire of prejudice and ignorance»
121. That he is
worth reading, is evident from his being read by all with pleasure;
they have the smallest share of it who use the dark glass of a
translation, those the highest, who enter into the spirit of the
original. They who are versed in languages cannot but know the
—134→
possibility of fully comprehending the import and meaning of
words, and yet find themselves utterly unqualified to express
themselves properly in their own. What Voltaire says of Hudibras,
that it is intraduisible, is applicable to almost every original composition
of wit, genius, and humour.
I flatter myself that my wonted perseverance will not fail me in adapting what I have already done to the use of a new edition, and that my zeal for the author will urge me on to the completion of such. At the same time I possess the highest reverence and esteem for that country which has produced so wonderful a genius, I can find no excuse for Father Feijoo's total silence of his name in his Glorias de España, of which he was so great an ornament. He was an honour not only to his country but to mankind, for I am certain from his writings, that of the two, his great genius and abilities were inferior to the goodness and honesty of the man. He is therefore to be regarded as a citizen of the world, and all have an interest of him.
In this state of things, I flatter myself with some hopes of
accomplishing what I have begun, not from the novelty, but from
the universality of my plan. I hope I have said enough to make my
scheme known, and shall think myself happy with your future
assistance and concurrence. I shall finish what I have at present to
offer nearly in the words of doctor Alphonso Villadiego in his
Advertencias to the edition of the Fuero juzgo, with some slight
variation: «He comentado este libro con mucho cuidado y diligencia,
empleando en ello muchos años de estudio, y revolviendo
muchos libros, pasando muchos trabajos, para ponerlo en punto.
Por lo menos merezco loa por haber intentado y salido con cosa
tan deseada, como lo es este libro, y por haber caminado por
donde nadie hasta hoy ha caminado, que es una de las mayores
dificultades que he tenido, en comentar y salir con esta obra. Y así
ya que no se me agradezca, no es razón haya desagradecimiento
de murmuración, considerando que aunque mi ingenio y erudición
no sea tanto como al parecer requirió obra tan singular y
—135→
peregrina, el mucho tiempo, estudio y trabajo y gran diligencia mía
podrá haberlo suplido, especialmente que no hay que agradecer al
que diere crédito y no a mí, pues no callo ninguno dellos, alegando
fielmente a cada uno en su lugar»
122. I have only to add that Cervantes
was himself sensible that his history would need a comment,
and has told us as much by the mouth of his hero, «que tendrá
necesidad de comento para entenderla»
(II, 3).
I am,
With Great Respect,
Your much obliged
and obedient Servant,
JOHN BOWLE.
Idemestone123,
April 18, 1776.
—136→
Don Gregorio Mayáns, in his Life of Cervantes, informs us that some persons have been so capricious as to suppose that the author meant to represent the Emperor Charles the Fifth, whilst others, without any the least grounds, were of opinion that he designed the Cardinal Duke of Lerma as the object of his satire. Amidst the uncertainty of guesses, if I am not peremptory and dogmatical, you will with your wonted candour receive my reveries and conjecture, that Ignacio Loyola might have been pitched upon by the author, as a person worthy of distinguished notice from him. In a word, it has been justly remarked of him by a late French writer, that he was as famous in his spiritual knighterrantry, as his illustrious countryman Don Quijote was in his quest of adventures124.
This is not the idle flourish of a Frenchman's pen, but is fairly
deducible from Rivadeneira's account of him, from a fair and
candid examination of which a just parallel betwixt both may be
formed. We find Loyola in the earlier part of his life extravagantly
fond of romances: «muy curioso y amigo de leer libros profanos de
caballerías»
. These he changed for the lives of saints commonly
called Flos sanctorum, which he read with that zeal that he determined
at once to imitate, and put in practice what he read: «y a
querer imitar y obrar lo que leía»
. Just in the same manner our
knight resolved to imitate as far as to him appeared possible the
passages which he had read in his books: «imitar en todo cuanto a
él le parecía posible los pasos, que había leído en sus libros»
(I, 4).
The impulse from his first reading so much affected Loyola that he
still blended his romances with his pious institute, and as a new
knight of Christ, in strict conformity to the practice of his brethren
—137→
in these histories, actually watched his arms, partly on foot, partly
kneeling before the image of Our Lady of Monserrate125.
The conduct of Loyola was in several instances truly quixotic,
as will appear by comparing the several historians. As he was
travelling to Monserrate, he happened to meet with a Moor who
spoke rather irreverently of the Holy Virgin, and who got the start
of him in his journey. He was much perplexed with his past
conversation with him, and was in doubt whether he should not
pursue him, and stab him for what he had said, but at length,
«después de haber buen rato pensado en ello, al fin se determinó de
seguir su camino hasta una encrucijada, de donde se partía el camino, y
allí soltar la rienda a la cabalgadura en que iba»
. Just in the same
manner Quijote, after his pleasing self-delusion upon his supposed
delivery of the boy Andrew, «llegó a un camino que en cuatro se
dividía, y luego se le vino a la imaginación las encrucijadas, donde
los caballeros andantes se ponían a pensar cuál camino de aquéllos
tomarían; y por imitarlos estuvo un rato quedo, y al cabo de haberlo
muy bien pensado, soltó la rienda a Rocinante»
.
It were very easy to pursue the similar behaviour of both these
worthies in this particular; but let us see how far the heroism of the
former was of a piece with the doctrine delivered by our knight
respecting the great article of complaints from pain occasioned by
wounds, that knights-errant are not to complain of any wound,
though their guts come through it: «no es dado a los caballeros
andantes quejarse de herida alguna, aunque se les salgan las tripas
por ella»
(I, 8). The wounding of Loyola at the siege of Pampeluna
in his legs is a fact well known, but his undergoing the operation
of having his leg broke again from the unskilfulness of his
surgeons, is not so: «Porque ni mudó color, ni gimió, ni suspiró, ni
hubo siquiera un ay, ni dijo palabra que mostrase flaqueza»
(Rivadeneira, Vida, cap. 1). He showed the same courage when he
submitted to a voluntary excruciating torment of the amputation
—138→
of a bone that he might wear his boot genteelly. This indeed was
previous to his conversion.
On this event his character is complete; what the old Marques
of Mantua resolved on -«de nunca peinar mis canas, ni las barbas
me tocare»
, which Sancho told his master he had related to him to
Dulcinea, I, 31, «y sin peinarse las barbas»
- the same did Loyola,
and let his nails grow too. One would be almost induced to think
this last circumstance the particular object of Cervantes's ridicule,
as among the other whimsical counsels to Sancho, one is to cut his
nails, and not suffer them to grow -«que te cortes las uñas, sin
dejarlas crecer»
- which particulars are carefully related of him by
his pupil the historian above-mentioned: «y el cabello traíale
desgreñado y por peinar, y con el menosprecio de si dejó crecer las
uñas y barba; que así suele Nuestro Señor trocar los corazones a los
que trae a su servicio, y con la nueva luz que les da, les hace ver las
cosas como son, y no como primero les parecían»
. To deny man the
use of those senses which God gave him is somewhat truly
quixotic; 'tis substituting fancy and imagination in the place of that
evidence which alone is to be relied on, from a due use and
exertion of them. The visionary enthusiast may give into the belief
of every absurdity, bewilder himself with his own strange notions,
«y ponerse en un laberinto de imaginaciones»
, because he will not
believe his own eyes, as was the case with the knight and Carrasco
(II, 14).
In forming parallels, matters may possibly be carried too far. But the treatment of Loyola in one instance greatly resembles that of Quijote on his delivery from the cuadrilleros, or troopers, by the curate (I, 46). On his return home to Spain from Jerusalem, he chanced to be travelling in Lombardy, and to come to a town besieged by his countrymen, to whom he appeared as one out of his senses, and the captain before he was brought was violently enraged with the soldiers who had taken him as a spy, rating them and telling them they were fools enough themselves for bringing hither a fool, and immediately ordered them to take him away and thrust him out. The soldiers, provoked with this treatment of their captain, vented their resentment on the poor pilgrim, giving him much ill language and loading him with kicks and cuffs. He used afterwards to relate that he then thought upon the insults and —139→ mocks offered to Christ by Herod and the soldiers, which was admirable comfort to him126.
But, to drop this subject, and to come to the proposed work. In
what is past I have all along insisted on a correct text. This
naturally requires an explanation of difficult passages, which
makes a principal part of the notes, and these, besides pointing out
the historical and other references, will in various places show a
propriety in the original absolutely untransferable into any other
language. From the collations of the original, and the London
edition of 1738, I was naturally led to reflect on the remissness or
want of skill in Pineda, and in so doing, I think myself justifiable
by the conduct of the judicious editor of the Canterbury Tales of
Chaucer. «The strange license»
, says he, «in which Mr. Urrey
appears to have indulged himself, of lengthening and shortening
Chaucer's words according to his own fancy, and of even adding
words of his own, without giving the readers the least notice, has made
the text of Chaucer in his edition by far the worst that was ever
published»
127.
To what I had said respecting the language of Cervantes, I
have this to add, that he has uniformly given a peculiar diction to
Sancho, and to correct his mistakes is an egregious error. This
Pineda did, for I find this reading in no edition before his, in the
following passage where Sancho is recollecting himself, and where
his repetitions have undoubted merit. «'Así es,' dijo Sancho.
'Luego, si mal no me acuerdo, proseguía, si mal no me acuerdo, 'el
llego, y falto de sueño y el ferido besa a V. M. las manos'»
. In his
edition it stands thus: «"Así es", dijo Sancho. "Luego, si mal no me
acuerdo proseguía: 'El llagado, y falto de sueño, y el ferido besa a
V. M. las manos'"».
128 Such arbitrary innovations in the text show a
—140→
want of taste in the editor, and must disgust the curious reader.
I have only to add that the several words explained, which constitute the glossary, will be found in their respective places among the annotations, and where any one is frequently used, it may be easily found in the general indexes; specimens of which are here annexed.
As to these, as they give an exact idea of the whole, I am to observe that the paging corresponds with the original MS.; that the * after the name shows the word to be used in both parts. See Quiñones, Quintanar, Quintañona, &c. The * after the page to be a part of the head of the chapter. See Quijote, C. 1. C. 2. -The stroke- between the lines indicates a repetition of the word: - preceding a name a different person of the same. See Quijada. C. Cavallero, Ca. Cavalleria, Cas. Cavallerias. P. 1. Primera Parte P. 2. Segunda parte. The passage in italics shows it to be verse. See P. 2. Libia, Loja, Renca.
The article Quijote, besides what is here produced, consists of eleven pages -the second follows immediately the former, so that an exact summary is formed of every chapter in both parts. Sancho's in like manner is between eight and nine.
—[141]→